Have you ever logged into your email, social media, or bank account and suddenly wondered,
“Is my password safe?”
If yes, you are already one step ahead of many people.
Most of us use the internet every single day. We shop online, send emails, post on social media, store personal photos, and even manage money using digital apps. All of this important information is protected by just one thing — a password. Yet, surprisingly, many people do not give their passwords much thought until something goes wrong.
Maybe you have heard about a friend whose social media account got hacked. Or maybe you received a strange login alert from an app you use often. In some cases, people lose money, private photos, or even their online identity — all because of a weak or reused password. These situations are more common than you might think.
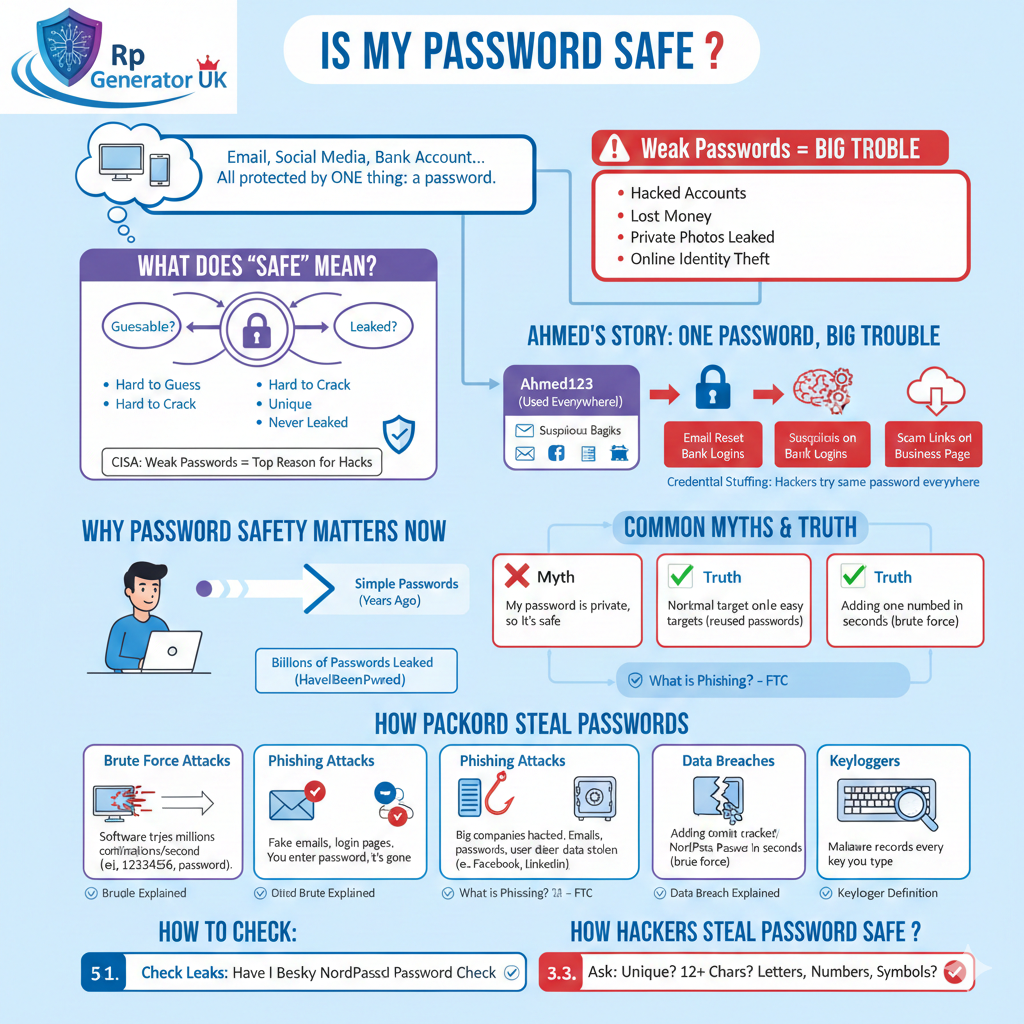
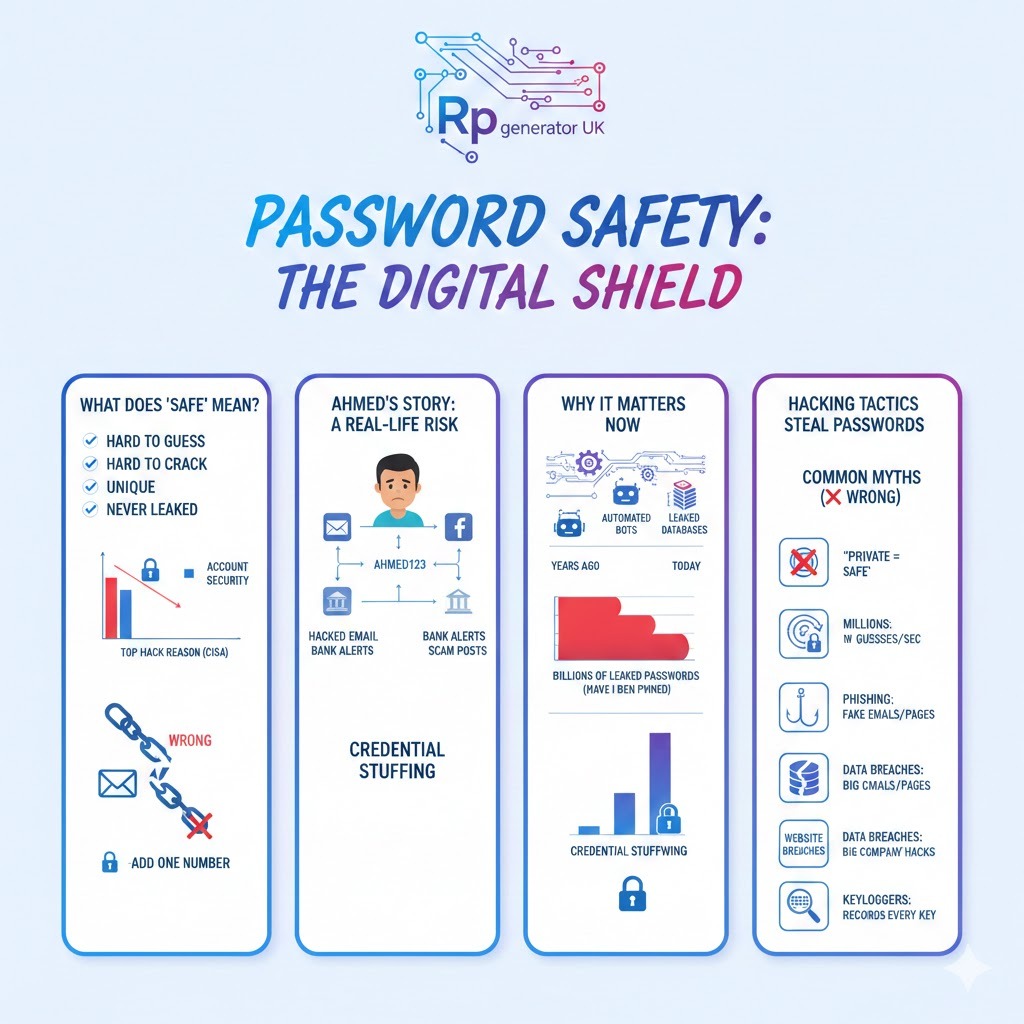
What Does “Is My Password Safe” Really Mean?
When we ask “Is my password safe?”, we are really asking:
- Can someone guess my password?
- Can my password be cracked by software?
- Is my password already leaked online?
- If one account is hacked, will all my accounts be hacked?
A safe password is one that:
- Is hard to guess
- Is hard to crack
- Is unique
- Has never been leaked
According to Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), weak passwords are one of the top reasons accounts get hacked.
A Short Real-Life Story: How One Weak Password Caused Big Trouble
Let me tell you a short story.
Ahmed, a small business owner, used the same password everywhere:
Ahmed123
It was easy to remember. He used it for:
- Bank account
- Online store
One day, his Facebook account was hacked. Within hours:
- His email was reset
- His bank received suspicious login attempts
- His business page posted scam links
Why?
Because hackers tried the same password everywhere.
This is called credential stuffing.
Why Password Safety Is More Important Than Ever
Years ago, passwords were simple. Today, hackers use:
- Automated bots
- AI-powered cracking tools
- Massive leaked databases
According to Have I Been Pwned, billions of passwords have already been leaked.
That means:
Your password might already be exposed—and you don’t even know it.
Common Myths About Password Safety (And the Truth)
Let’s clear some confusion.
Myth 1: “My password is private, so it’s safe”
❌ Wrong
If a website is hacked, your password can be leaked even if you did nothing wrong.
Myth 2: “Hackers target only big people”
❌ Wrong
Hackers love normal users because:
- They reuse passwords
- They don’t use protection
- They are easy targets
Myth 3: “Adding one number makes it strong”
❌ Wrong
A password like Password1 is cracked in seconds using brute force attacks.
How Hackers Actually Steal Passwords (In Simple Words)
Let’s break this down.
1. Brute Force Attacks
Hackers use software that tries:
- 123456
- password
- qwerty
- millions of combinations per second
Learn more:
👉 Brute Force Explained
2. Phishing Attacks
You receive:
- Fake emails
- Fake login pages
- Fake messages
You enter your password, and boom—it’s gone.
Example resources:
- What is Phishing? – FTC
3. Data Breaches
Big companies get hacked.
Hackers steal:
- Emails
- Passwords
- User data
Examples:
- Yahoo
Learn more:
👉 Data Breach Explained
4. Keyloggers
Malware records:
- Every key you type
- Every password you enter
Learn more:
👉 Keylogger Definition
How to Check: Is My Password Safe Right Now? (Step-by-Step)
Let’s get practical.
Step 1: Check if Your Password Was Leaked
Use:
👉 Have I Been Pwned Password Check
This tool checks your password without exposing it.
Step 2: Test Password Strength
Try:
These tools show:
- Crack time
- Strength level
Step 3: Ask These Questions
- Is my password unique?
- Is it 12+ characters?
- Does it include letters, numbers, symbols?
If not, it’s time to change it.
What Makes a Password Strong? (Easy Explanation)
A strong password has:
✔ Length
✔ Randomness
✔ Uniqueness
✔ Complexity
Weak Password Example
nginx
Copy code
Ali123
Strong Password Example
perl
Copy code
Ali!Rain$Blue#92
Even better? Use a passphrase.
What Is a Passphrase and Why It’s Safer
A passphrase is a group of random words.
Example:
Copy code
Horse-Battery-River-Moon
Why it’s safer:
- Long
- Easy to remember
- Hard to crack
How to Create a Strong Password (Step-by-Step Guide)
Step 1: Start With Random Words
Choose 3–4 unrelated words.
Step 2: Add Numbers and Symbols
Mix things up.
Step 3: Make It Unique
Never reuse it.
Step 4: Store It Safely
Use a password manager.
Should I Use a Password Manager? (Short Answer: Yes)
A password manager:
- Creates strong passwords
- Stores them securely
- Autofills logins
Popular options:
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Even if your password is stolen, Two-Factor Authentication stops hackers.
It adds:
- SMS code
- App code
- Fingerprint
Enable it everywhere possible.
Signs Your Password Is Not Safe
Watch out for:
- Login alerts you didn’t request
- Password reset emails
- Unknown devices logged in
- Locked accounts
If you see these, act immediately.
What To Do If Your Password Is Compromised
Step 1: Change password immediately
Step 2: Enable 2FA
Step 3: Check other accounts
Step 4: Scan your device for malware
Use:
👉 Malwarebytes
Password Safety for Mobile Users
Phones are not immune.
Tips:
- Lock your phone
- Avoid public Wi-Fi
- Use app locks
Learn more:
👉 Mobile Security Tips – Google
Password Safety for Businesses and Freelancers
If you:
- Work online
- Handle client data
- Run websites
Then password safety is not optional.
Follow:
- Unique passwords
- Password managers
- Employee training
Why Reusing Passwords Is Extremely Dangerous
One leaked password = all accounts hacked.
This is why unique passwords are critical.
Learn more:
👉 Credential Stuffing Explained
Future of Passwords: Are Passwords Going Away?
Some companies now use:
- Passkeys
- Biometrics
- Hardware keys
But passwords are still here—for now.
Final Checklist: Is My Password Safe?
Ask yourself:
✔ Is it long?
✔ Is it unique?
✔ Is it random?
✔ Is 2FA enabled?
✔ Is it stored securely?
If you answered no to any, change it today.
Conclusion: Your Password Is Your Digital Key
Think of your password like:
- Your house key
- Your car key
- Your wallet
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Is My Password Safe?
1. How do I know if my password is safe?
A password is safe if it is long, unique, random, and not reused on other websites. You can also check if it was leaked using trusted tools like Have I Been Pwned.
2. What is considered a weak password?
A weak password is short, easy to guess, or common, such as 123456, password, admin, or your name with numbers.
3. Is using the same password on multiple sites dangerous?
Yes, very dangerous. If one website gets hacked, hackers can access all your other accounts using the same password.
4. Can hackers really guess my password?
Yes. Hackers use automated tools that can try millions of passwords per second, especially if your password is short or common.
5. Are long passwords safer than short ones?
Yes. Longer passwords are much harder to crack. A password with 12–16 characters is far safer than one with 6–8 characters.
6. What is a passphrase and why is it safer?
A passphrase is a group of random words, like Blue-Coffee-River-Clock. It is easier to remember and much harder to crack.
7. Is adding numbers and symbols enough to make a password strong?
Not always. Adding just one number or symbol is not enough. The password must also be long and unpredictable.
8. Can my password be stolen even if I never share it?
Yes. Passwords can be stolen through data breaches, malware, or fake login pages without you sharing them directly.
9. What is a data breach?
A data breach happens when hackers break into a website or company system and steal user data, including passwords and emails.
10. What is phishing and how does it steal passwords?
Phishing is a scam where attackers trick you into entering your password on a fake website or link that looks real.
11. How often should I change my passwords?
Change your passwords:
- If they were leaked
- If you notice suspicious activity
- At least once a year for important accounts
12. Is it safe to save passwords in my browser?
Browser password saving is convenient, but password managers are safer because they encrypt your data better.
13. What is a password manager?
A password manager is a tool that stores your passwords securely and helps create strong, unique passwords for every account.
14. Are password managers really safe?
Yes, when you choose a trusted one. They use strong encryption and are much safer than reusing passwords.
15. What happens if my password is leaked online?
Hackers may try:
- Logging into your email
- Resetting other accounts
- Stealing personal or financial data
16. How can I check if my password was leaked?
You can use trusted services like Have I Been Pwned to see if your password or email appears in known breaches.
17. What is two-factor authentication (2FA)?
2FA adds an extra step like a code or fingerprint, making your account safer even if your password is stolen.
18. Should I enable 2FA on all accounts?
Yes, especially on:
- Email accounts
- Social media
- Banking and payment apps
19. Are mobile passwords safer than desktop passwords?
Not automatically. Mobile passwords are safe only if you use:
- Screen locks
- App locks
- Updated software
20. Can public Wi-Fi steal my password?
Yes. Unsecured public Wi-Fi can allow attackers to spy on your data. Avoid logging into important accounts on public networks.
21. What is a brute force attack?
A brute force attack is when software tries many password combinations until the correct one is found.
22. Can antivirus software protect my passwords?
Antivirus helps block malware and keyloggers, but it cannot fix weak or reused passwords.
23. Is writing passwords on paper safe?
Only if you keep them in a very secure place. However, password managers are usually safer and more practical.
24. Are biometric logins like fingerprint safer than passwords?
Biometrics are convenient and add security, but they usually work together with passwords, not instead of them.
25. What should I do if someone logs into my account without permission?
Immediately:
- Change your password
- Enable 2FA
- Log out of all devices
- Check account activity
26. Can hackers crack passwords instantly?
Weak passwords can be cracked in seconds. Strong, long passwords can take years or even centuries to crack.
27. Is “password123” really that bad?
Yes. It is one of the most commonly hacked passwords and offers almost no protection.
28. Should children and elderly people also use strong passwords?
Yes. Everyone is a target. Simple but long passphrases work best for all age groups.
29. Are passwords going to disappear in the future?
Some services use passkeys and biometrics, but passwords are still widely used and important today.
30. What is the easiest way to stay safe with passwords?
Use:
- A password manager
- Unique passwords
- Two-factor authentication
- Regular security checks
This combination gives the best protection.