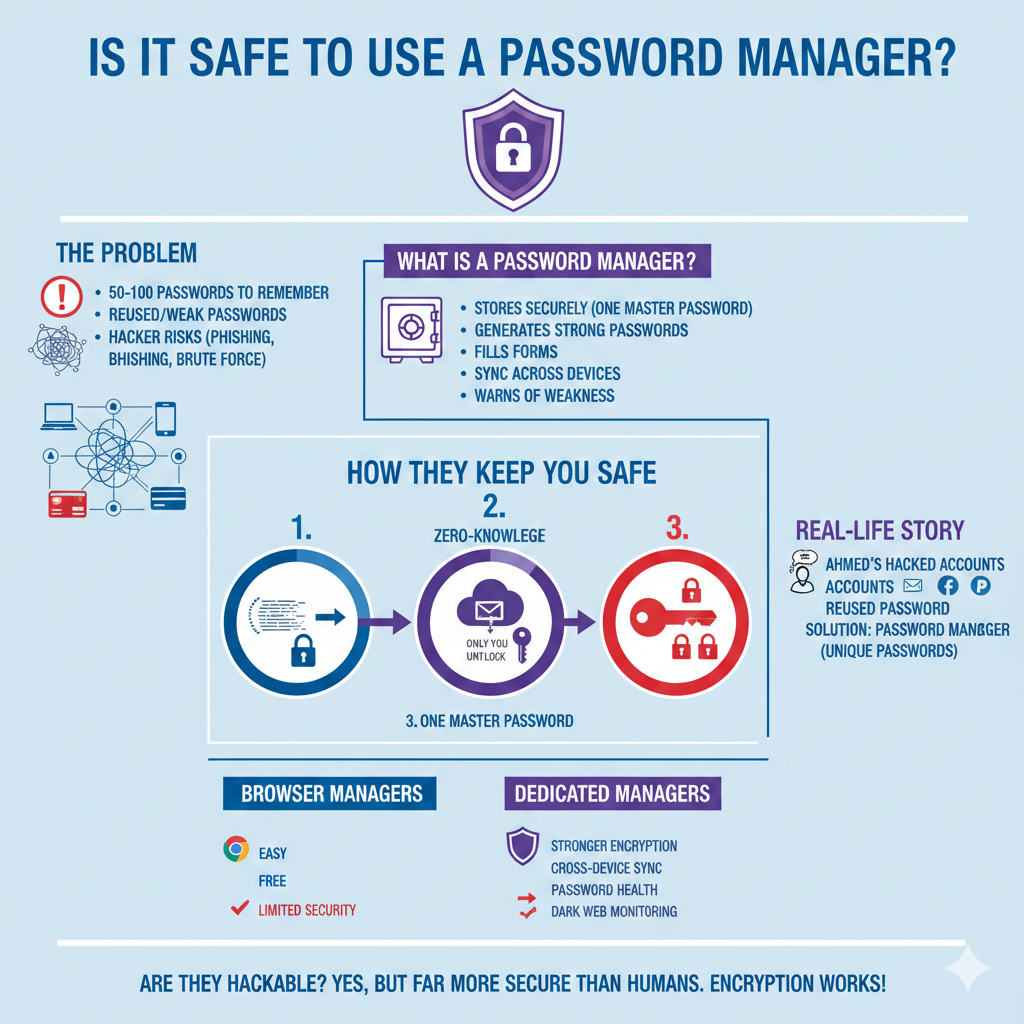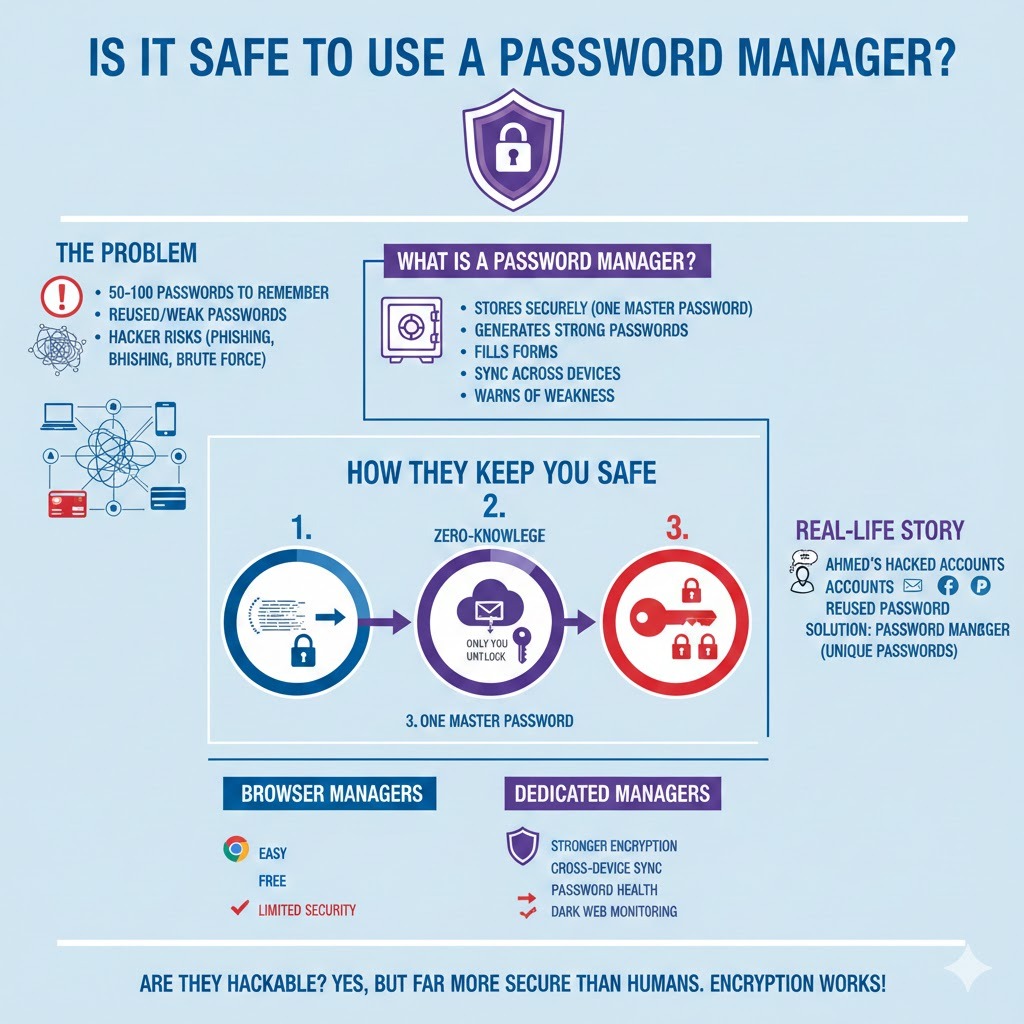
In today’s online world, passwords are everywhere. Email, social media, banking, shopping, work tools—everything asks for a password. Now imagine trying to remember 50–100 different strong passwords without writing them down. Sounds impossible, right?
This is exactly where a password manager comes in. But a very common and important question still remains:
Is it really safe to use a password manager?
We will talk honestly about how password managers work, their risks, their benefits, and how to use them safely.
We’ll also share real-life examples, step-by-step guidance, and finally, 30 detailed FAQs to clear up all your doubts.
What Is a Password Manager?
A password manager is a tool that stores your passwords securely in one place. Instead of remembering dozens of passwords, you only remember one master password.
Most password managers can:
- Save passwords securely
- Generate strong passwords automatically
- Fill login forms for you
- Sync across devices (mobile, laptop, tablet)
- Warn you if a password is weak or leaked
👉 Learn more from this trusted explanation: What is a Password Manager – Wikipedia
A Short Real-Life Story (Anecdote)
Ahmed runs a small online business. Like many people, he reused the same password on his email, Facebook, and PayPal. One day, a random website he signed up for got hacked. His password leaked.
Within hours:
- His Facebook was taken over
- His email was locked
- His PayPal showed suspicious activity
All because of one reused password.
Later, Ahmed started using a password manager. Today, every account has a unique, strong password, and he doesn’t even know most of them. He only remembers one.
This is not a rare story. It happens every day.
Why Passwords Alone Are No Longer Safe
Before asking whether password managers are safe, we must understand why traditional password habits are dangerous.
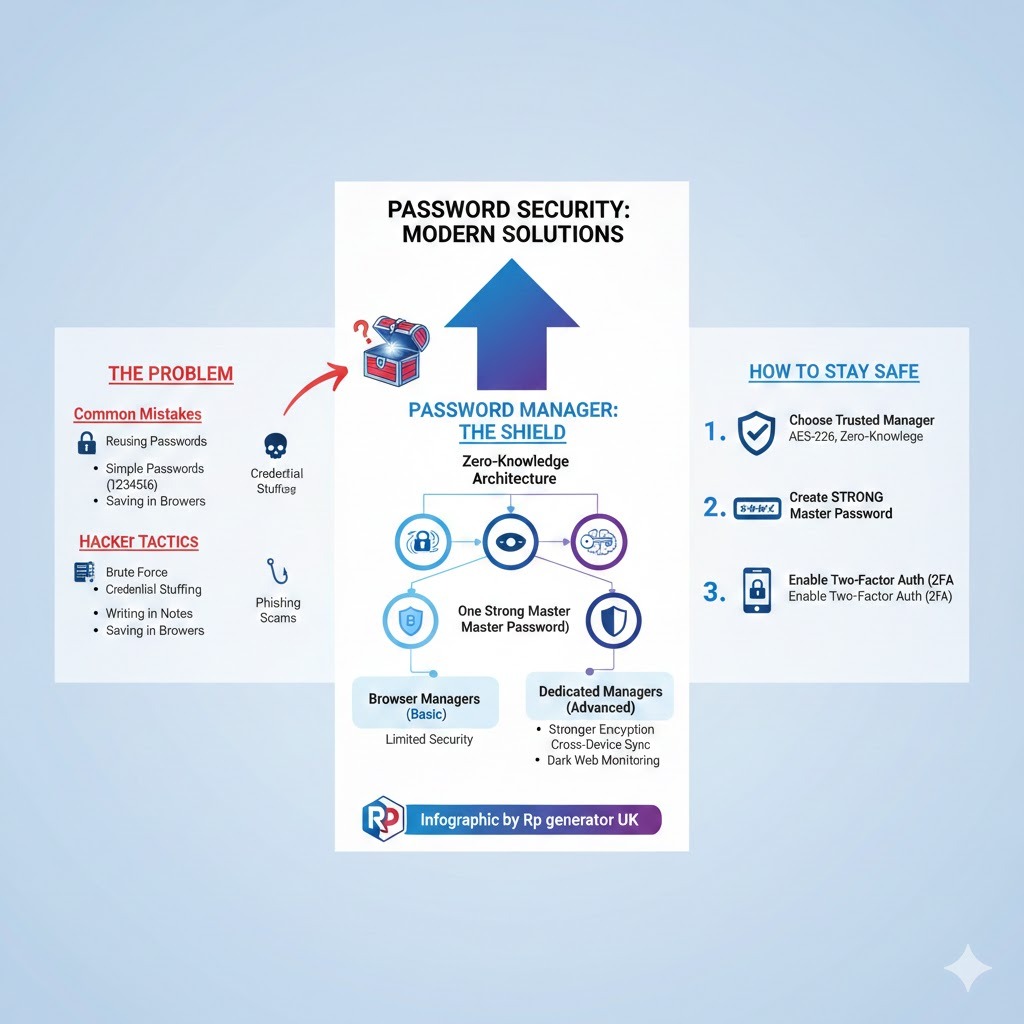
Common Password Mistakes People Make
Most people:
- Reuse the same password everywhere
- Use simple passwords like 123456, password, or name123
- Write passwords in notes or notebooks
- Save passwords in browsers without protection
👉 See real statistics here: Most Common Passwords – NordPass
Hackers Love Weak Passwords
Hackers use:
- Brute force attacks
- Credential stuffing
- Phishing scams
👉 Explanation: Credential Stuffing Attack
Without a password manager, you are already at risk.
How Does a Password Manager Keep You Safe?
Let’s break this down step by step, without technical jargon.
1. Encryption (The Core of Safety)
Password managers use encryption, which means your data is turned into unreadable code.
Even if someone steals the data, they cannot read it without your master password.
👉 explanation: What Is Encryption? – Cloudflare
2. Zero-Knowledge Architecture
Good password managers follow zero-knowledge security.
This means:
- Even the company cannot see your passwords
- Only you can unlock them
👉 Learn more: Zero-Knowledge Security – LastPass
3. One Strong Master Password
Instead of remembering many weak passwords, you remember one strong master password.
👉 Guide: How to Create a Strong Master Password
Are Password Managers Hackable?
This is the biggest fear people have.
The Honest Answer
👉 Yes, anything connected to the internet can be attacked.
But here’s the key difference:
- Password managers are far more secure than human memory
- They use strong encryption, not plain text
- A breach does not mean passwords are readable
👉 Real-world explanation: Are Password Managers Safe? – Kaspersky
Real Example: When a Manager Is Breached
Some password managers have faced breaches. However:
- Encrypted vaults remained protected
- Users with strong master passwords stayed safe
This shows encryption works.
Browser Password Managers vs Dedicated Password Managers
Many people ask:
“Is saving passwords in Chrome or Firefox enough?”
Browser Managers (Pros & Cons)
Pros:
- Easy to use
- Free
Cons:
- Limited security controls
- Less encryption transparency
- Vulnerable if device is compromised
👉 Comparison: Browser vs Password Manager – Bitwarden
Dedicated Password Managers (Better Option)
They offer:
- Stronger encryption
- Cross-device syncing
- Password health reports
- Dark web monitoring
Step-by-Step: How to Use a Password Manager Safely
Step 1: Choose a Trusted Password Manager
Look for:
- Strong encryption (AES-256)
- Zero-knowledge policy
- Good reputation
👉 Trusted list: Best Password Managers – Wirecutter
Step 2: Create a Very Strong Master Password
Use:
- 12–16+ characters
- Mix of words, numbers, symbols
Example:
BlueHorse$River!92
👉 Tool: Strong Password Generator
Step 3: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra security layer.
Even if someone knows your master password, they still can’t log in.
👉 Learn more: What Is Two-Factor Authentication – Authy
Step 4: Replace Weak and Reused Passwords
Most managers show:
- Weak passwords
- Reused passwords
- Compromised passwords
Fix them one by one.
Step 5: Keep Your Devices Secure
- Use screen lock
- Update software
- Avoid public computers
👉 Basic guide: Device Security Tips – FTC
Advantages of Using a Password Manager
1. Strong Unique Passwords Everywhere
No more reuse. Every account is protected.
2. Saves Time and Mental Stress
No more “Forgot Password?” clicks.
3. Protection Against Phishing
Password managers won’t auto-fill on fake websites.
👉 Learn: What Is Phishing? – Google
4. Secure Sharing
Share passwords safely with family or teams.
Possible Risks (And How to Avoid Them)
Risk 1: Weak Master Password
Solution: Make it strong and unique.
Risk 2: Device Malware
Solution: Use antivirus and updates.
Risk 3: Human Error
Solution: Enable 2FA and backups.
Are Free Password Managers Safe?
Many free managers are safe and open-source.
Examples:
- Bitwarden
- KeePass
👉 Open-source security explained: What Is Open Source Software – Red Hat
Who Should Definitely Use a Password Manager?
- Online shoppers
- Freelancers
- Business owners
- Students
- Remote workers
Basically: Anyone who uses the internet.
Final Verdict: Is It Safe to Use a Password Manager?
Short Answer:
👉 Yes. Using a password manager is far safer than not using one.
When used correctly, password managers:
- Reduce hacking risks
- Protect your digital identity
- Save time and stress
The real danger is reusing weak passwords, not password managers.
30 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are password managers 100% safe?
No system is 100% safe, but password managers are among the safest options available.
2. Can hackers access my passwords?
Not without your master password and 2FA.
3. What happens if I forget my master password?
Most managers cannot recover it due to zero-knowledge security.
4. Are password managers better than browser saving?
Yes, they offer stronger security and features.
5. Can password managers be hacked?
Systems can be attacked, but encrypted data stays protected.
6. Is using one master password risky?
No, if it’s strong and unique.
7. Are free password managers safe?
Yes, many are safe and open-source.
8. Do password managers work offline?
Some, like KeePass, do.
9. Can I use them on mobile?
Yes, most support Android and iOS.
10. Are password managers legal?
Yes, completely legal worldwide.
11. Can employers see my passwords?
No, personal vaults are private.
12. Do password managers sell data?
Reputable ones do not.
13. Are password managers safe for banking?
Yes, they are recommended for banking security.
14. Can I store credit cards securely?
Yes, most support encrypted storage.
15. Do password managers protect against phishing?
Yes, they help detect fake websites.
16. What is zero-knowledge encryption?
It means only you can access your data.
17. Can I share passwords safely?
Yes, via secure sharing features.
18. Are password managers safe for families?
Yes, many offer family plans.
19. How often should I change passwords?
Only when weak or compromised.
20. Are password managers hard to use?
No, they are beginner-friendly.
21. Do I need antivirus with a password manager?
Yes, they work best together.
22. Can password managers generate passwords?
Yes, strong and random ones.
23. Are password managers safe on public Wi‑Fi?
Yes, but avoid logging in on shared devices.
24. Can I export my passwords?
Yes, most allow encrypted export.
25. Are password managers safe for businesses?
Yes, many businesses rely on them.
26. What if the company shuts down?
You can usually export your vault.
27. Do password managers slow devices?
No, they are lightweight.
28. Are password managers worth paying for?
Yes, for advanced security features.
29. Can I use multiple password managers?
Yes, but it’s not recommended.
30. Should beginners use a password manager?
Absolutely. They are made for beginners.
Final Thought
Using a password manager is one of the smartest digital safety decisions you can make today. It’s secure, and proven to protect millions of users worldwide.
If you care about your online safety, a password manager is not optional anymore—it’s essential.