Introduction: Why This Question Matters More Than Ever
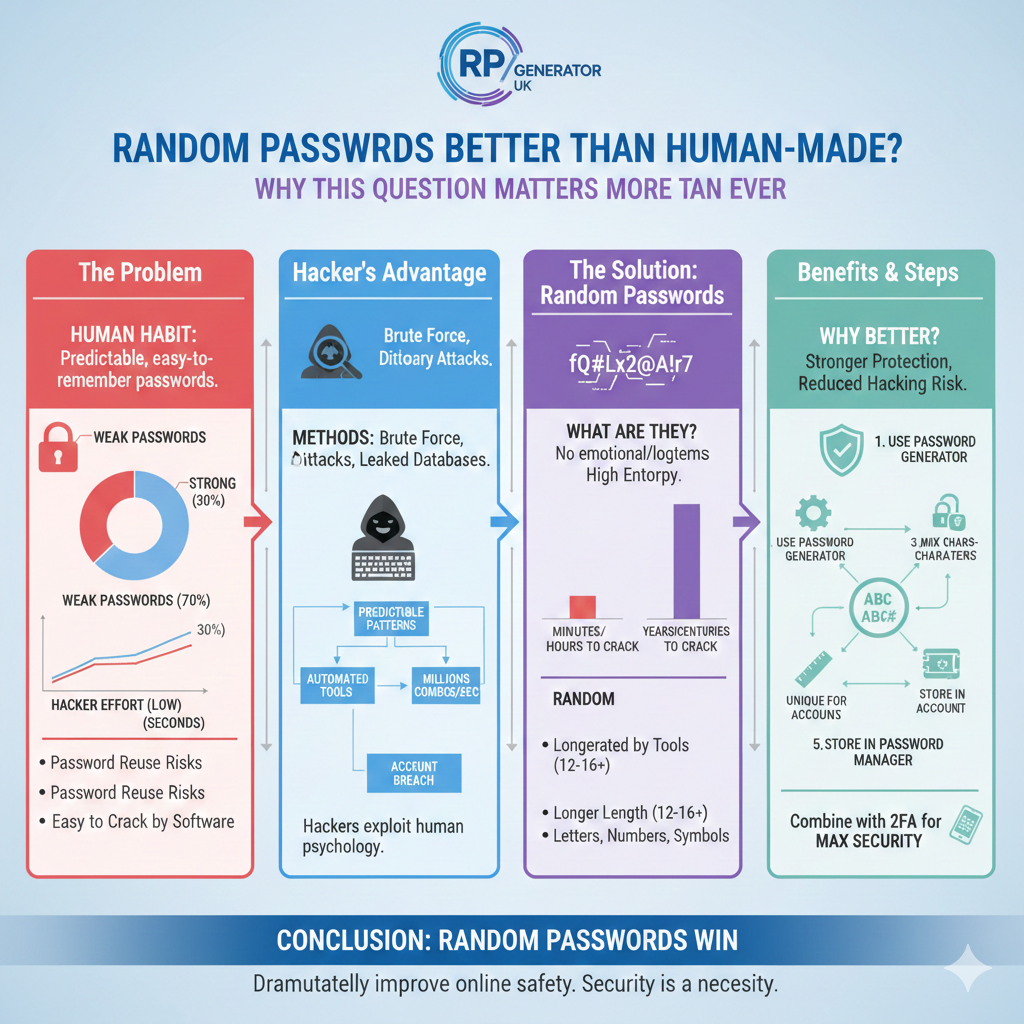
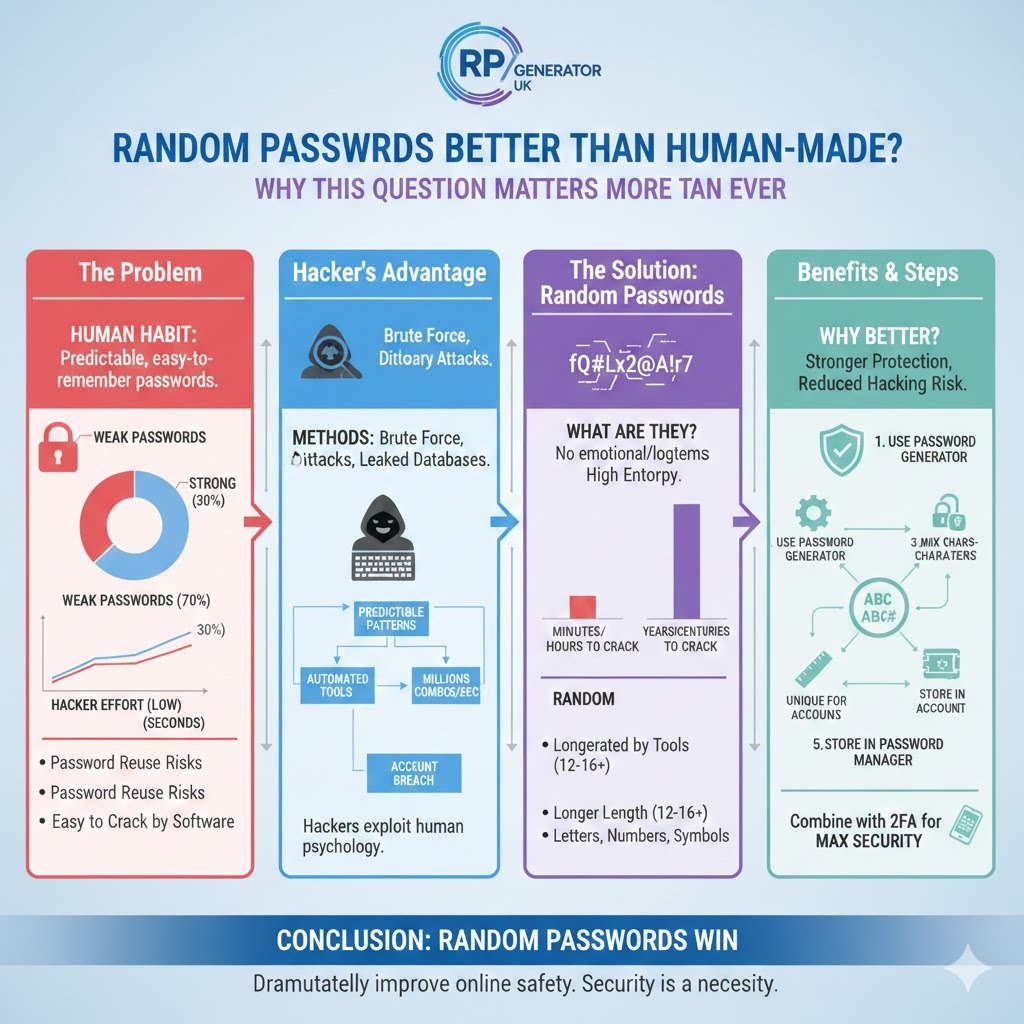
Have you ever created a password and felt confident because it included your name, a birthday, or maybe your favourite football team? You are not alone. Most people believe they create good passwords, but sadly, many of those passwords fall into the category of weak passwords. In today’s digital world, where almost every part of life depends on online accounts, this small mistake can cause big problems. This is exactly why the debate around random passwords VS human-made passwords has become so important.
Every day, millions of accounts are attacked using methods like brute force attacks and password cracking. Hackers do not sit and guess passwords like humans do. Instead, they use powerful software that can test millions of password combinations in seconds. When people rely on predictable passwords, they unknowingly make the hacker’s job easier. This puts online password security, account password security, and even personal data at serious risk.
On the other hand, random passwords are created without emotional or logical patterns. They do not rely on names, dates, or common words. Because of this, they offer stronger password protection and better password safety. In this article, we will clearly explain whether random passwords are better than human-made ones, using real-world examples, simple explanations, and practical steps. By the end, you will fully understand why random passwords are safer, how they work, and how you can use them easily in daily life.
The Human Habit of Creating Passwords (And Why It Often Fails)
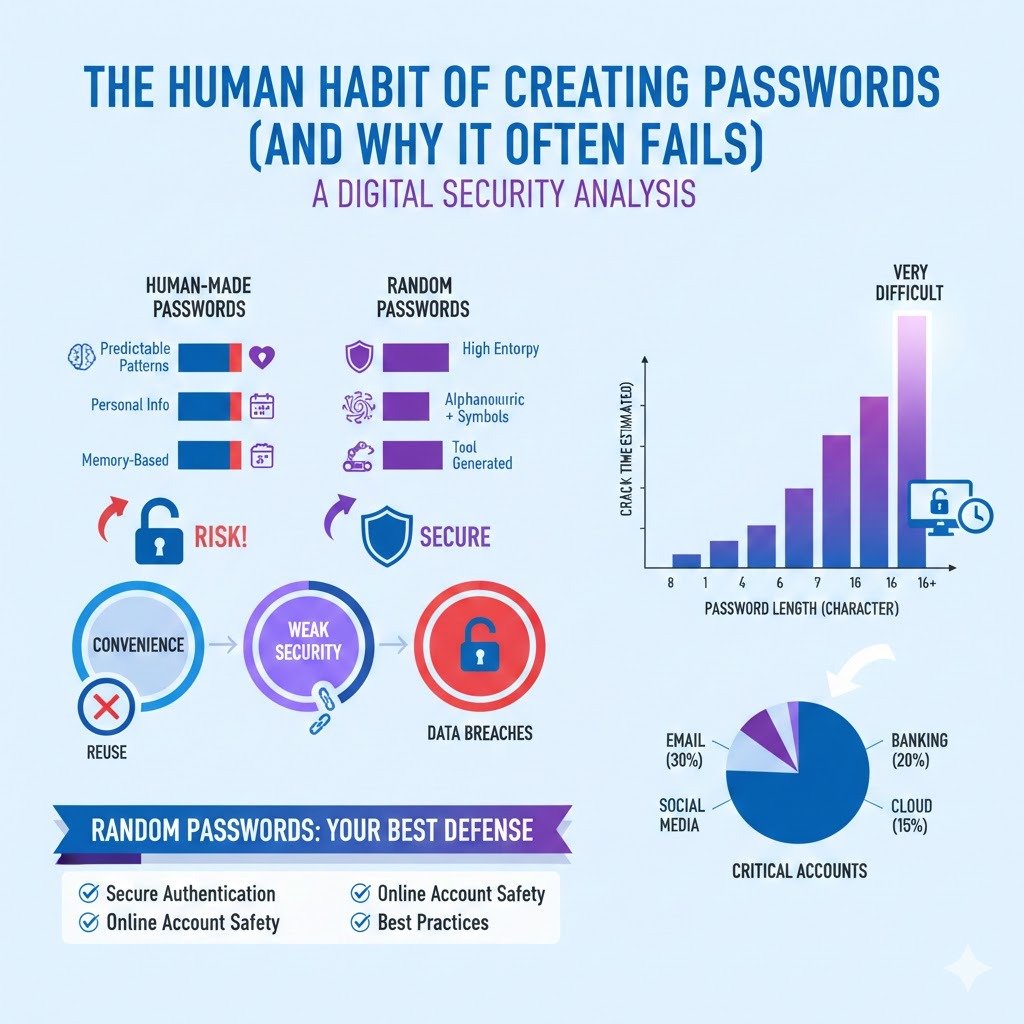
Let us start with a truth: humans are not good at randomness. When creating human-made passwords, most people choose something meaningful or easy to remember. This could be a pet’s name, a child’s birthday, or a simple word followed by numbers like “Password123.” While this feels safe, it actually creates serious password security risks. Hackers understand human behaviour very well. They know how people think, and they use this knowledge to break passwords faster.
Studies on human psychology show that people prefer convenience over complexity. This is why password reuse risks are so common. One password is often used across email, social media, and banking accounts. If just one account is breached, attackers can access many others. This is a major issue in digital security passwords and a leading cause of data breach prevention failures.
Another problem is password patterns. Humans like structure, such as capital letters at the beginning and numbers at the end. Hackers design tools that target these patterns first. This makes human-made passwords security risks very high. Even when people try to create a strong password, they often unknowingly follow predictable rules.
Because of these habits, human memory vs password security becomes a losing battle. The easier a password is to remember, the easier it usually is to crack. This is where random passwords clearly outperform human-created ones and provide better password attack prevention.
What Are Random Passwords and Why Are They Different?
Random passwords are passwords created using complete randomness, without relying on meaningful words or personal information. They are usually generated by random password generator tools that combine letters, numbers, and symbols in unpredictable ways. This randomness gives them high password entropy, which is a key factor in password strength.
Unlike human-made passwords, random passwords do not follow emotional or logical patterns. For example, a random password like “fQ9#Lx2@A!r7” has no connection to your life. Because of this, it becomes extremely difficult for hackers to guess or crack. This is why security experts strongly recommend random passwords for online accounts, especially for email, banking, and cloud services.
Another major advantage is password length and password complexity. Random password generators allow you to create long passwords easily. Length plays a huge role in resisting password guessing and brute force attacks. Even adding a few extra characters can multiply the time required to crack a password.
In simple terms, random passwords explained in simple terms means letting a tool do the hard work instead of relying on your brain. This dramatically improves secure authentication, online account safety, and overall cybersecurity best practices.
Random Passwords vs Human-Made Passwords:
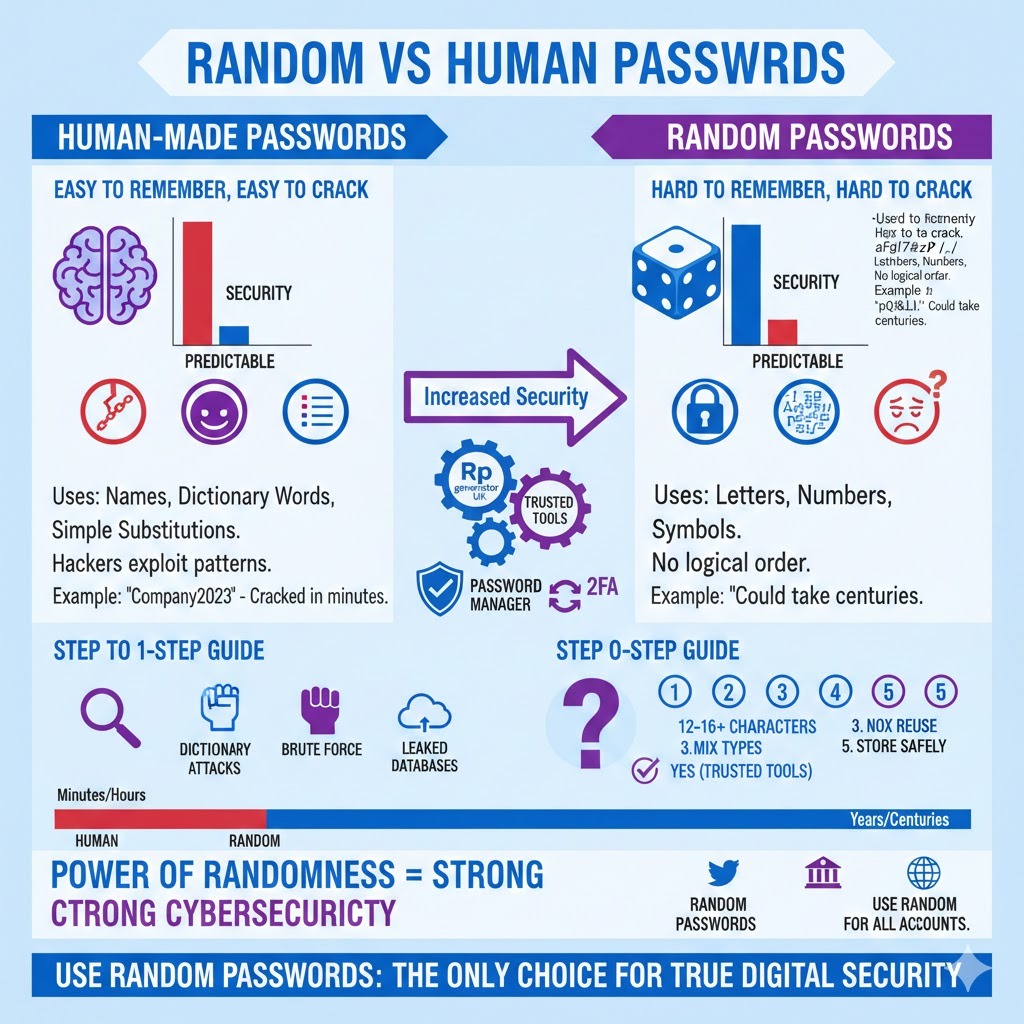
When comparing random passwords vs human created passwords, the difference becomes very clear. Human passwords are built for memory. Random passwords are built for security. This single difference changes everything. Hackers exploit human behaviour, not machines. They know how humans think, but they struggle against true randomness.
Human-made passwords often fall into categories such as names, dictionary words, or simple substitutions like “@” instead of “a.” These are well-known common password mistakes. Attack tools are designed to test these combinations first. This makes how hackers crack human passwords much easier than most people realize.
Random passwords, however, do not follow password patterns. They significantly reduce password hacking risks. Even advanced cracking tools struggle because there is no logical order to test. This is why random passwords reduce hacking risk and improve password protection tips.
A simple example: a human password might take minutes or hours to crack. A truly random password of sufficient length could take years or even centuries. This is the power of password randomness, importance and password entropy explained simply.
A Real-Life Story: When a Simple Password Caused Big Trouble
Let me share a real-world style example. A small business owner once used the password “Company2023” for their email. It seemed reasonable and easy to remember. Unfortunately, this is a textbook case of predictable passwords. A hacker used automated tools targeting common patterns and gained access within minutes.
Once inside, the attacker reset passwords on connected services, accessed invoices, and even sent fake payment requests to clients. This is a classic example of password reuse risks combined with weak password basics. The damage was not just financial but also reputational.
After this incident, the owner switched to random passwords for email security and used a password manager. Since then, there have been no security issues. This simple change dramatically improved online password security and account password security.
Stories like this highlight why strong passwords matter and clearly show why random passwords are recommended by security experts worldwide.
How Hackers Actually Attack Passwords (In Simple Words)
Understanding how hackers guess passwords helps explain why random passwords win. Hackers use methods like dictionary attacks, brute force attacks, and leaked password databases from previous breaches. Human-made passwords often appear in these databases, especially when people reuse them.
Tools automatically test millions of combinations per second. They start with common words, names, and patterns. This is why are human passwords are predictable, not a question but a fact. Humans repeat the same mistakes again and again.
Random passwords stop these attacks early. Because there is no pattern, hackers must test every possible combination. This makes attacks slower and often impractical. This is a major win for password attack prevention and cybersecurity passwords.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Create Strong Random Passwords
Creating strong random passwords is easier than most people think.
Step 1: Use a trusted password generator tool such as Bitwarden or LastPass.
Step 2: Choose a password length of at least 12–16 characters.
Step 3: Include letters, numbers, and symbols for better password complexity.
Step 4: Never reuse the same password. This avoids password reuse risks.
Step 5: Store passwords safely using a password manager.
This method ensures secure login passwords, better password management, and strong password storage safety.
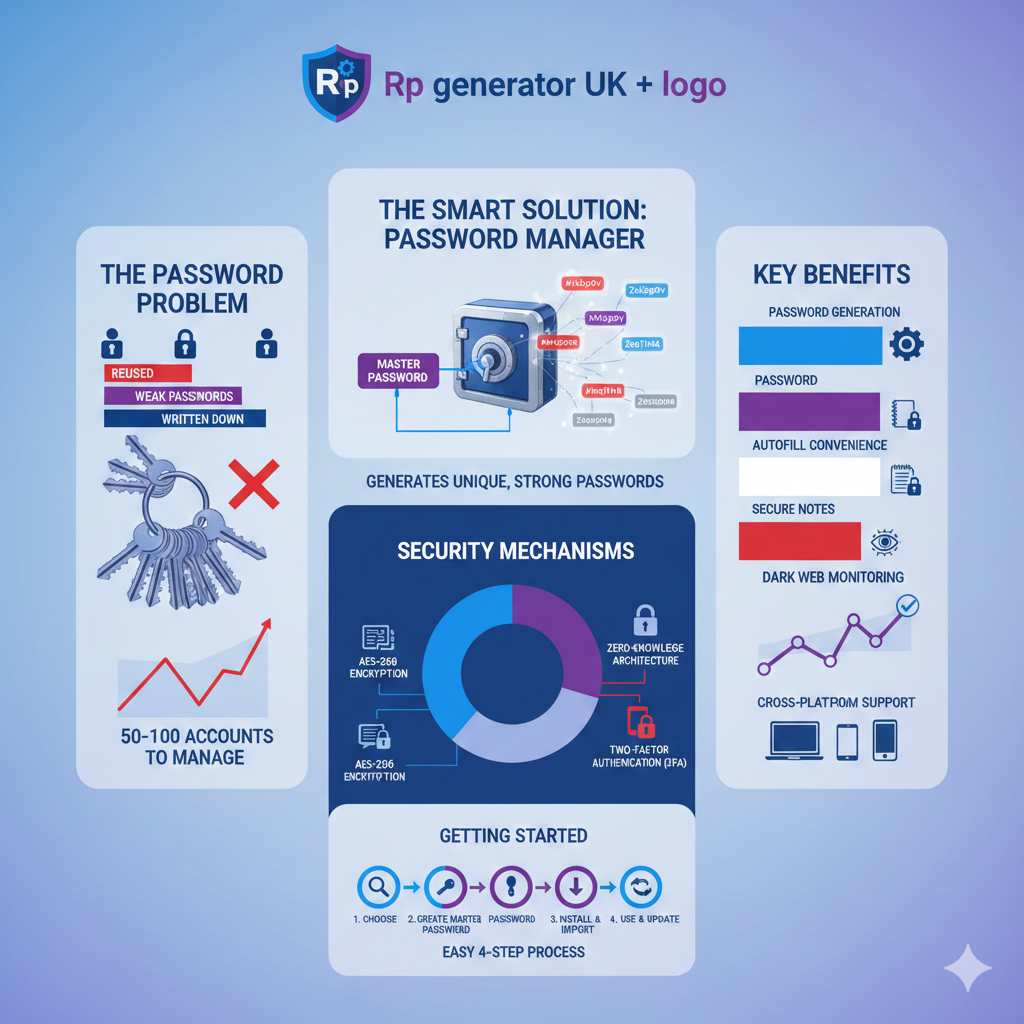
Are Password Generators Safe to Use?
Many users ask, are password generators safe to use? The short answer is yes, if you use trusted tools. Reputable generators create passwords locally and do not store them. This ensures secure authentication and protects against leaks.
Avoid unknown websites and always check privacy policies. Using reliable tools is a core part of cybersecurity best practices.
Random Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
While random passwords are powerful, combining them with two-factor authentication creates even stronger password protection. Even if a password is compromised, 2FA blocks access.
This combination is ideal for random passwords and data breach prevention, especially for banking and email accounts.
Common Myths About Random Passwords
Many believe random passwords are impossible to manage. This is a myth. With modern password managers, usability is easy. Others think long passwords are unnecessary. In reality, how long a random password is matters greatly for security.
Random Passwords for Different Accounts
Use random passwords for social media, random passwords for banking accounts, and random passwords for maximum security in all important areas. Each account deserves unique protection.
Conclusion: Are Random Passwords Better Than Human-Made?
The answer is clear and backed by real-world evidence. Yes, random passwords are better than human-made passwords. Humans are predictable. Hackers exploit predictability. Randomness breaks this cycle. By using random passwords, you dramatically improve online account safety, reduce password hacking risks, and follow proven password best practices.
In today’s digital world, security is not optional. It is a necessity. Choosing random passwords is one of the simplest yet most powerful steps you can take toward true password safety for online users and long-term digital security passwords.
FAQs About: Are Random Passwords Better Than Human-Made?
1. Are random passwords better than human-made passwords?
Yes, random passwords are better than human-made passwords because they do not follow predictable patterns. This makes them much harder to guess or crack.
2. Why are random passwords safer than human passwords?
Random passwords have higher password entropy, meaning they contain more unpredictable combinations, which improves password security.
3. What is the biggest weakness of human-made passwords?
The biggest weakness is predictability. Humans often use names, dates, or common words, creating weak passwords.
4. How do hackers crack human-made passwords?
Hackers use brute force attacks, dictionary attacks, and leaked password lists to guess common human password patterns.
5. What is a random password generator?
A random password generator is a tool that creates strong, unpredictable passwords using letters, numbers, and symbols.
6. Are password generator tools safe to use?
Yes, trusted password generator tools are safe and recommended for better online password security.
7. Why do people still choose weak passwords?
People prefer convenience and memory over security, which leads to common password mistakes.
8. What is password entropy in simple terms?
Password entropy means how unpredictable a password is. Higher entropy equals stronger password protection.
9. Can random passwords prevent brute force attacks?
Yes, random passwords significantly slow down brute force attacks, making them ineffective in most cases.
10. Are long passwords more secure than short ones?
Yes, greater password length increases security and reduces password cracking risks.
11. How long should a random password be?
A strong random password should be at least 12–16 characters for maximum security.
12. Why is password reuse dangerous?
Password reuse risks allow hackers to access multiple accounts if one password is compromised.
13. Are human-made passwords ever safe?
They can be safer if long and complex, but they still cannot match the strength of random passwords.
14. What makes a password strong?
A strong password is long, random, unique, and contains mixed characters.
15. Are random passwords hard to remember?
Yes, but using a password manager removes the need to remember them.
16. What is a password manager?
A password manager securely stores and autofills passwords, improving password management and safety.
17. Do random passwords protect against data breaches?
They reduce risk, especially when combined with two-factor authentication, improving data breach prevention.
18. Why do security experts recommend random passwords?
Experts recommend them because they provide better secure authentication and resist cyber attacks.
19. Can random passwords be guessed?
In theory yes, but in practice it would take years or centuries, making attacks unrealistic.
20. Are random passwords good for email security?
Yes, random passwords for email security are highly recommended because email controls many other accounts.
21. Should I use random passwords for social media?
Yes, social media accounts are common targets, so random passwords for social media are important.
22. Do symbols really make passwords stronger?
Yes, symbols increase password complexity and make cracking more difficult.
23. Are common words bad for passwords?
Yes, dictionary words are easily guessed and lead to predictable passwords.
24. What are the most common human password mistakes?
Using names, dates, simple patterns, and reusing passwords across accounts.
25. Can random passwords stop cyber attacks completely?
No, but they greatly reduce risk when used with other cybersecurity best practices.
26. What is the difference between strong and weak passwords?
Strong passwords are random and long; weak passwords are short and predictable.
27. Why is randomness important in password security?
Password randomness removes patterns that hackers rely on, increasing protection.
28. Should every account have a different password?
Yes, unique passwords are essential to avoid password reuse risks.
29. Are random passwords suitable for beginners?
Yes, especially with password managers, they are ideal for password security for beginners.
30. What is the best password creation method today?
Using a random password generator with a password manager is the best and safest method.