We will explain how password keepers work, how safe they really are, real-life stories, step-by-step guides, risks, benefits, and how to choose the right one.
By the end, you will clearly know whether a password keeper is safe for you.
What Is a Password Keeper?
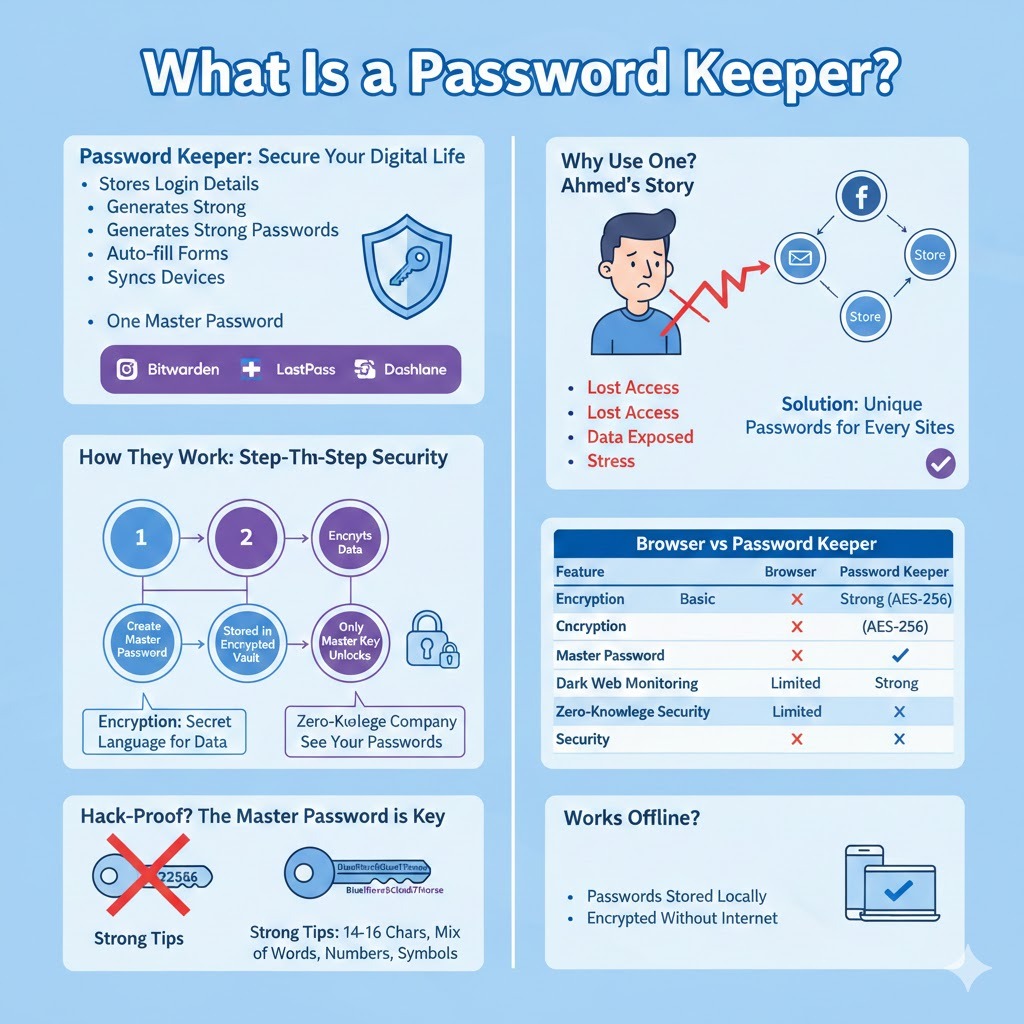
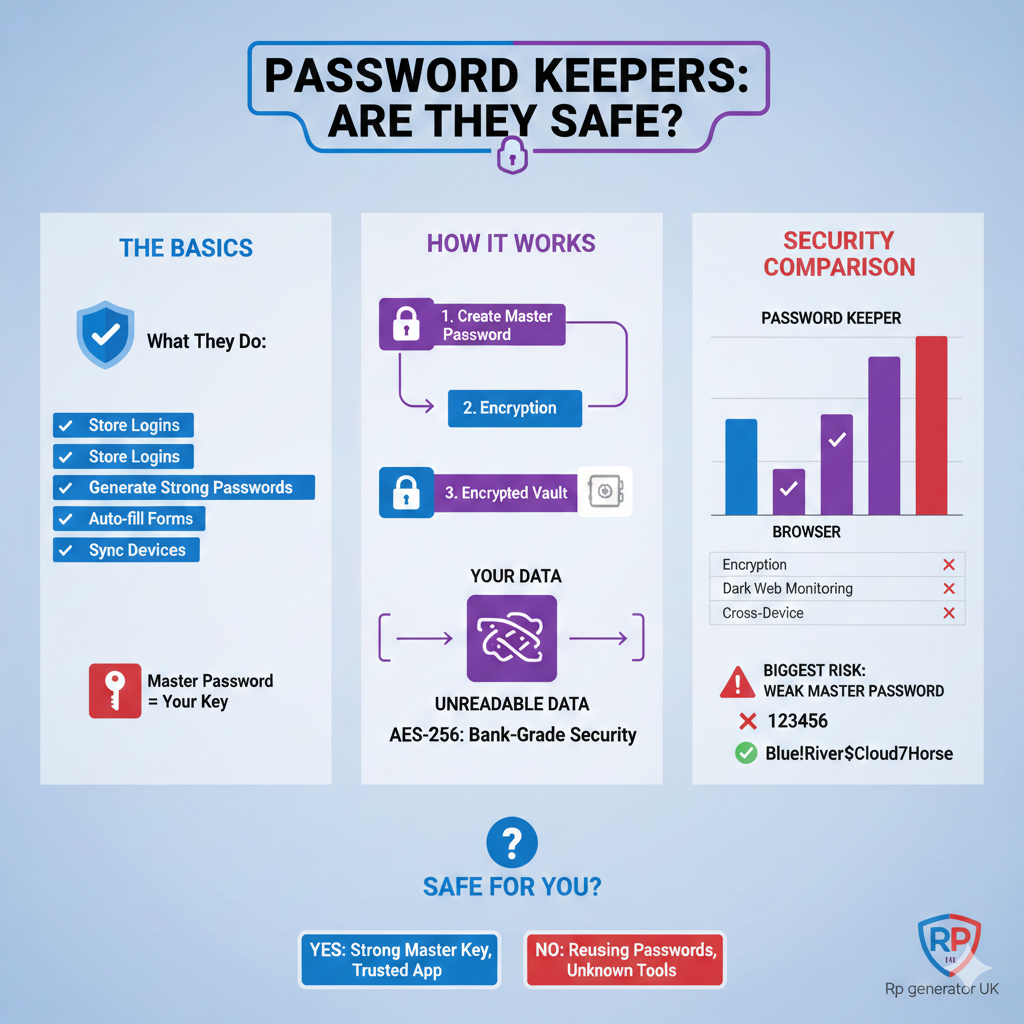
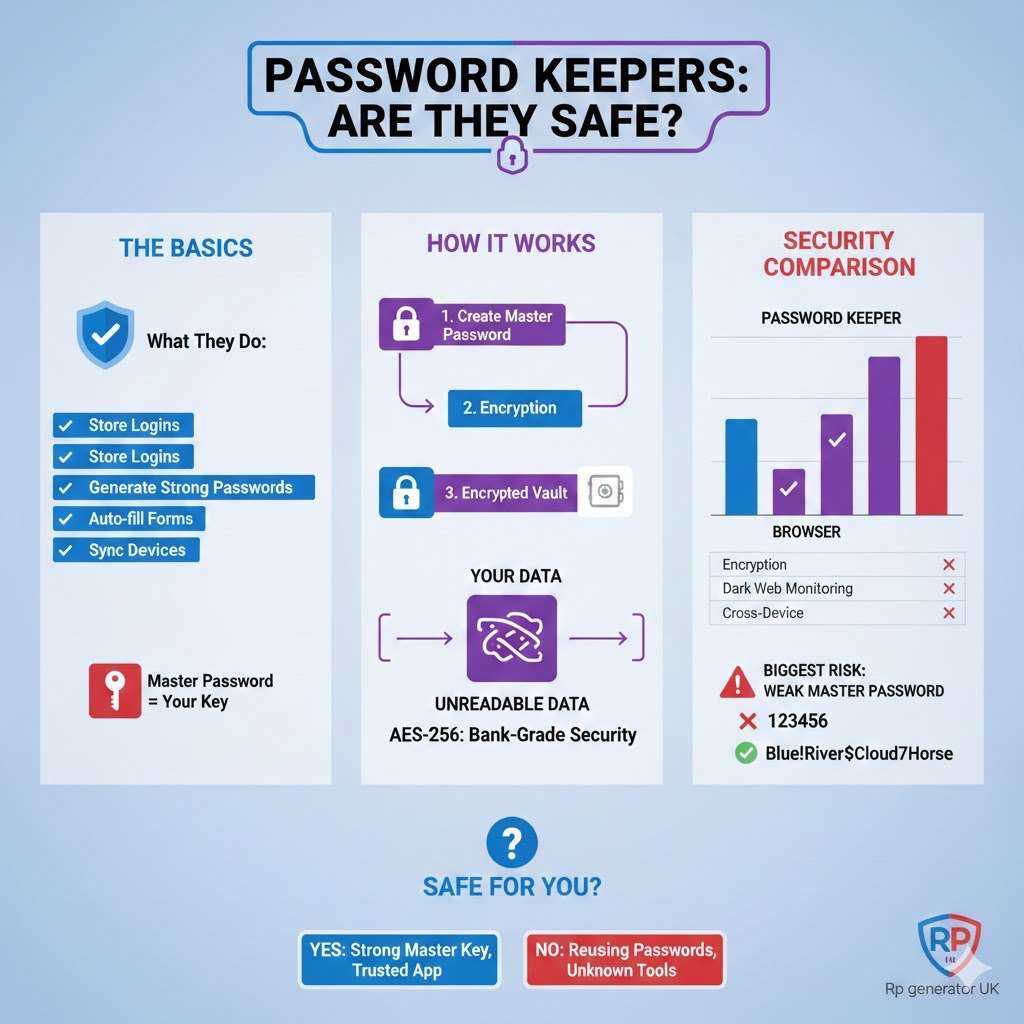
A password keeper is a tool that stores your login details securely. Instead of writing passwords on paper or reusing the same password everywhere, you save them in one protected place.
Most password keepers:
- Store usernames and passwords
- Generate strong passwords for you
- Auto-fill login forms
- Sync across devices
- Protect everything with one master password
Popular examples include tools like Bitwarden, 1Password, LastPass, and Dashlane.
🔗 Learn more about password managers here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Password_manager
Why Do People Use Password Keepers?
Let’s start with a small story.
A Real-Life Example
Ahmed, a small business owner, used the same password for his email, Facebook, and online store. One day, his email was hacked through a leaked database. Within hours, the attacker reset his Facebook and store passwords.
The result?
- Lost access to his accounts
- Customer data exposed
- Days of stress and recovery
This happened because password reuse is dangerous.
Password keepers solve this problem by allowing:
- Unique passwords for every site
- No need to remember them all
🔗 Why password reuse is risky: https://www.cisa.gov/password-tips
How Do Password Keepers Work?
Understanding how they work helps answer the safety question.
Step-by-Step: How a Password Keeper Protects You
- You create a master password
- The password keeper encrypts your data
- Passwords are stored in an encrypted vault
- Only your master password can unlock it
- Even the company cannot see your passwords
This process uses encryption.
🔗 What is encryption? https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ssl/what-is-encryption/
What Is Encryption (In Simple Words)?
Encryption is like turning your data into a secret language.
Imagine writing a letter and locking it in a box. Only the person with the key can open it. Encryption works the same way — but digitally.
Most trusted password keepers use:
- AES-256 encryption (used by banks and governments)
🔗 AES-256 explained: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/AES
Are Password Keepers Safer Than Browsers?
Many people save passwords in their browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox). But browser password storage has limits.
Browser vs Password Keeper
| Feature | Browser | Password Keeper |
| Encryption | Basic | Strong (AES-256) |
| Master password | ❌ | ✅ |
| Dark web monitoring | ❌ | ✅ |
| Cross-device security | Limited | Strong |
| Zero-knowledge security | ❌ | ✅ |
🔗 Browser password risks: https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/password-manager
What Is Zero-Knowledge Security?
This is a very important concept.
Zero-knowledge means:
- The company cannot see your passwords
- Even if their servers are hacked, your data remains unreadable
This makes password keepers much safer than many other tools.
🔗 Zero-knowledge explained: https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/10/what-does-zero-knowledge-mean
Are Password Keepers Hack-Proof?
Short answer: Nothing is 100% hack-proof.
Long answer: Password keepers are extremely hard to break if used correctly.
Real Incident Example
In 2022, a major password manager suffered a security incident. Headlines scared users. But later analysis showed:
- Encrypted vaults remained secure
- Only users with weak master passwords were at risk
🔗 Why master passwords matter: https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/collection/top-tips-for-staying-secure-online/password-managers
The Biggest Risk: Weak Master Passwords
Your master password is the key to everything.
Bad Master Password Examples
- 123456
- password123
- yourname2024
Strong Master Password Tips
- At least 14–16 characters
- Mix of words, numbers, symbols
- Not used anywhere else
Example:
Blue!River$Cloud7Horse
🔗 How to create strong passwords: https://www.nist.gov/itl/applied-cybersecurity/tig/back-basics-multi-factor-authentication
Do Password Keepers Work Offline?
Yes, many do.
Offline access means:
- Passwords stored locally
- Encrypted even without internet
This adds another safety layer.
🔗 Offline password managers: https://bitwarden.com/help/offline-access/
Are Free Password Keepers Safe?
Yes — if they are reputable.
Trusted free options include:
- Bitwarden
- KeePass
However, avoid unknown tools with:
- No encryption info
- No security audits
- No transparency
🔗 Open-source password managers: https://www.privacyguides.org/en/password-managers/
Password Keepers vs Writing Passwords on Paper
Some people believe paper is safer.
The Truth
Paper passwords:
- Can be stolen
- Can be lost
- Cannot alert you to breaches
Password keepers:
- Encrypt data
- Monitor leaks
- Auto-update security
🔗 Physical vs digital password risks: https://www.consumerreports.org/digital-security/are-password-managers-safe/
Step-by-Step: How to Start Using a Password Keeper Safely
Step 1: Choose a Trusted Tool
- Check reviews
- Look for encryption details
Step 2: Create a Strong Master Password
- Never reuse it
Step 3: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Adds extra protection
🔗 What is 2FA? https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/access-management/what-is-two-factor-authentication/
Step 4: Import Existing Passwords
Step 5: Replace Weak Passwords
Do Password Keepers Protect Against Phishing?
Yes — and this is often ignored.
Password keepers:
- Only auto-fill on correct websites
- Refuse fake login pages
🔗 Phishing protection explained: https://www.phishing.org/what-is-phishing
Are Password Keepers Safe for Businesses?
Yes, many companies require them.
Benefits:
- Central access control
- Reduced breaches
- Better compliance
🔗 Business password security: https://www.cisa.gov/secure-our-world
What Happens If You Forget Your Master Password?
This is serious.
Most zero-knowledge tools:
- Cannot recover it
- This protects your privacy
Solution:
- Use recovery keys
- Store backup securely
🔗 Account recovery risks: https://support.1password.com/forgot-master-password/
Are Mobile Password Keepers Safe?
Yes, if your phone is secure.
Extra protections include:
- Fingerprint
- Face unlock
- Auto-lock vault
🔗 Mobile security basics: https://www.android.com/safety/
Common Myths About Password Keepers
Myth 1: Hackers target password keepers
Truth: They target weak passwords.
Myth 2: One password is risky
Truth: One strong master password is safer than many weak ones.
Myth 3: Password keepers sell data
Truth: Reputable tools follow zero-knowledge policies.
Are Password Keepers Worth It?
Yes — for most people.
They:
- Reduce stress
- Improve security
- Save time
🔗 Expert opinions: https://www.wired.com/story/best-password-managers/
Conclusion:
Yes, password keepers are safe — when used correctly.
They are:
- Safer than reusing passwords
- Safer than browsers
- Safer than notebooks
The key is:
- Choose a trusted tool
- Use a strong master password
- Enable extra security
If you do this, a password keeper becomes one of the strongest security tools you can use today.
FAQs: Are Password Keepers Safe?
1. Are password keepers safe to use?
Yes. Trusted password keepers are very safe when used correctly. They protect your passwords with strong encryption and lock everything behind one master password.
2. How do password keepers protect my passwords?
They encrypt your data before saving it. This means your passwords turn into unreadable code that only your master password can unlock.
3. Is a password keeper safer than using the same password everywhere?
Absolutely. Reusing passwords is very risky. A password keeper lets you use a different strong password for every site.
4. Can hackers hack password managers?
Hackers can try, but modern password managers use encryption that makes stolen data useless without the master password.
5. What happens if a password manager company is hacked?
In most cases, your passwords stay safe because they are encrypted. With zero-knowledge security, even the company cannot see your data.
6. What is a master password?
A master password is the main password you use to unlock your password vault. It should be long, strong, and never reused anywhere else.
7. What if I forget my master password?
Most secure password keepers cannot recover it for you. This protects your privacy, so it’s important to store recovery keys safely.
8. Are free password keepers safe?
Yes, many free password keepers are safe, especially well-known or open-source ones. Avoid unknown apps with no security information.
9. Are paid password managers more secure than free ones?
Not always, but paid versions often offer extra features like dark web monitoring, family sharing, and advanced security tools.
10. Are browser password managers safe?
They are better than nothing, but dedicated password keepers are usually more secure and offer stronger protection.
11. Do password keepers store passwords online?
Some use cloud storage, but your data is encrypted before it is uploaded. Even the service provider cannot read your passwords.
12. Can password keepers work offline?
Yes. Most password managers allow offline access, keeping your passwords stored securely on your device.
13. Are password keepers safe on mobile phones?
Yes, especially when your phone is protected with a PIN, fingerprint, or face unlock. Many apps also auto-lock the vault.
14. Can password managers protect against phishing?
Yes. They only auto-fill passwords on the correct websites, helping you avoid fake or phishing pages.
15. Do password keepers generate strong passwords?
Yes. They can create long, random passwords that are very hard for hackers to guess or crack.
16. Are password keepers safe for online banking?
Yes. Security experts often recommend using password managers for banking because they reduce human mistakes.
17. Can beginners easily use password keepers?
Yes. Most password managers are designed for everyday users and offer simple setup steps and guides.
18. Are password keepers good for elderly users?
Yes. They reduce the need to remember many passwords and make logging in easier with auto-fill features.
19. Do password managers slow down devices?
No. They are lightweight and usually have no noticeable impact on device performance.
20. Can password keepers store more than passwords?
Yes. Many can store secure notes, credit card details, Wi-Fi passwords, and personal information safely.
21. Are open-source password managers safer?
Open-source tools allow experts to review the code, which can increase trust. Both open-source and closed-source tools can be safe.
22. Do companies and businesses use password managers?
Yes. Many businesses require employees to use password managers to reduce security risks and data breaches.
23. Can password keepers detect leaked passwords?
Many password managers monitor data breaches and alert you if your passwords or email appear in a leak.
24. Is one master password really enough?
Yes, if it is strong and unique. One strong master password is safer than many weak passwords.
25. Can governments access my password vault?
With zero-knowledge encryption, no one can access your vault without your master password.
26. Are password keepers safe for families?
Yes. Many offer family plans that allow secure password sharing with trusted members.
27. Can I export my passwords from a password keeper?
Yes. Most password managers allow secure export so you can move to another service if needed.
28. Do password managers protect against keyloggers?
They reduce risk by limiting how often you type passwords, but full protection depends on overall device security.
29. Are password keepers safer than writing passwords on paper?
Yes. Paper can be lost or stolen easily, while password keepers encrypt and protect your data digitally.
30. Should everyone use a password keeper?
For most people, yes. Password keepers improve security, save time, and make online life much safer.